Knowledge graphs project
Experimenting with knowledge graphs and RAG applications
Introduction
Goal of the project: I am trying to leverage knowledge graphs to create an interactive database. I am implementing a user interface with streamlit.
How it works:
- put some text in a textbox
- run the process button
- data gets converted into graph objects in a multi-step process, using LLMs.
- you can inspect the objects
- click a button to push the new objects to database
- switch to the query page
- query in natural language, a LLM transforms the query into cypher query and runs it against the DB
Stack:
- Python
- langchain (LLMs, retrieval chains)
- Neo4j (graphDB)
- streamlit (UI)
- MistralAI (LLMs)
Preliminary results
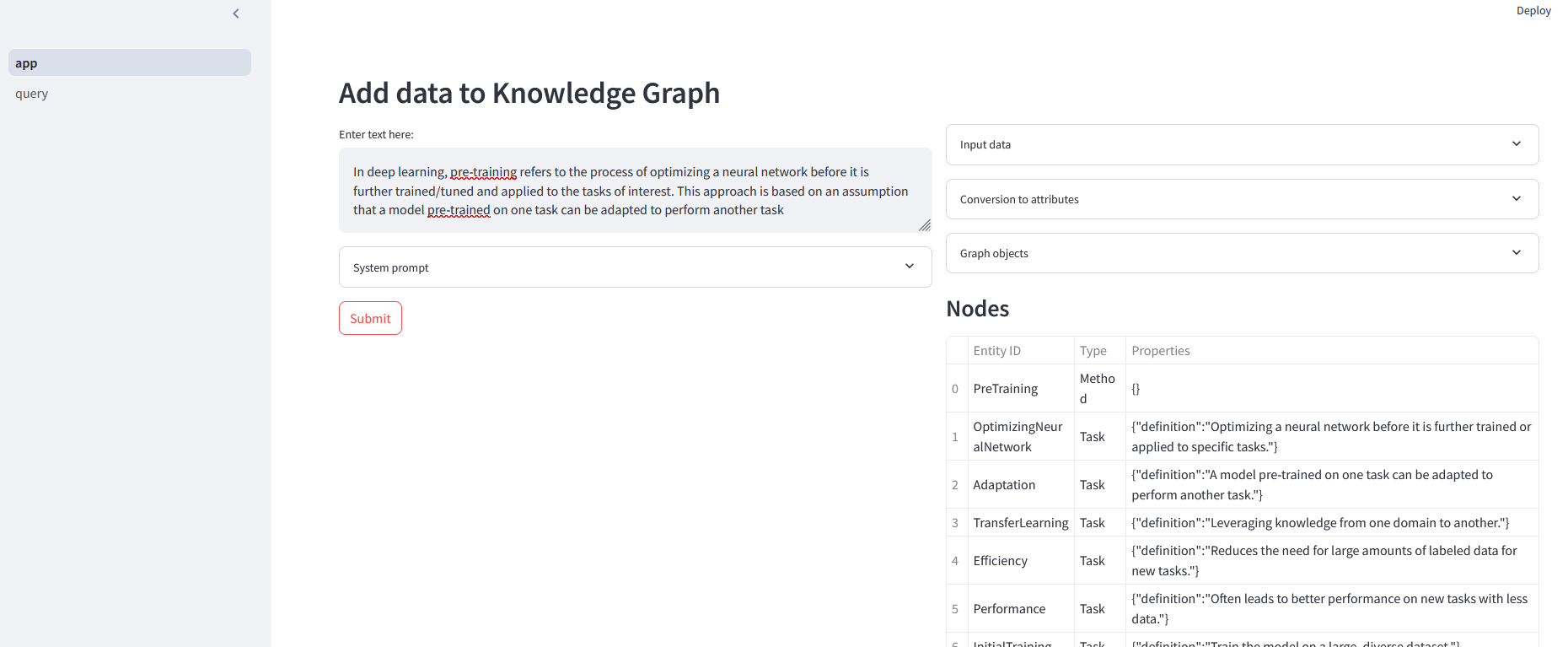
I gave some input text to ingest:
In deep learning, pre-training refers to the process of optimizing a neural network before it is further trained/tuned and applied to the tasks of interest. This approach is based on an assumption that a model pre-trained on one task can be adapted to perform another task
The text gets processed and converted into graph objects:
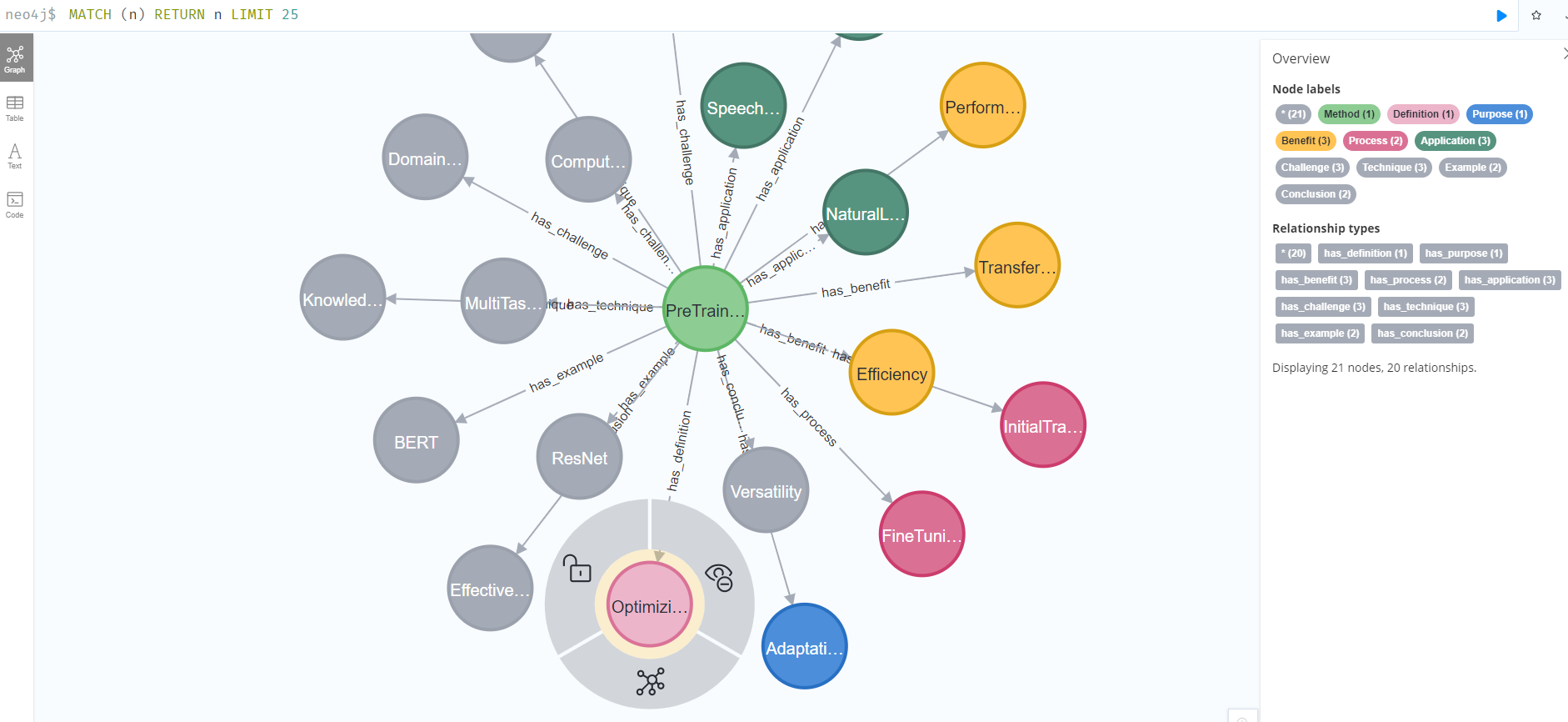
We can see the resulting graph in the Neo4j UI:
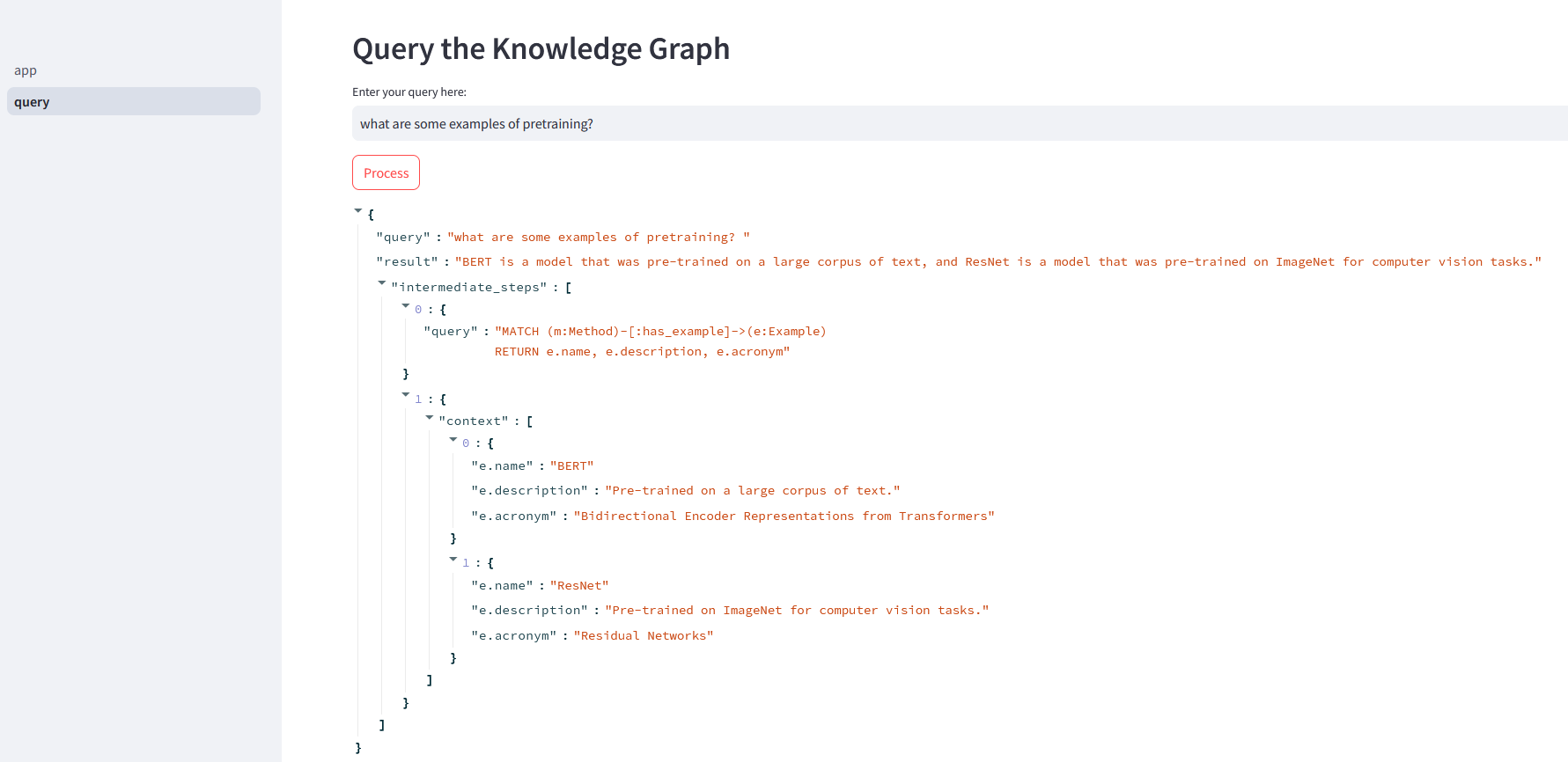
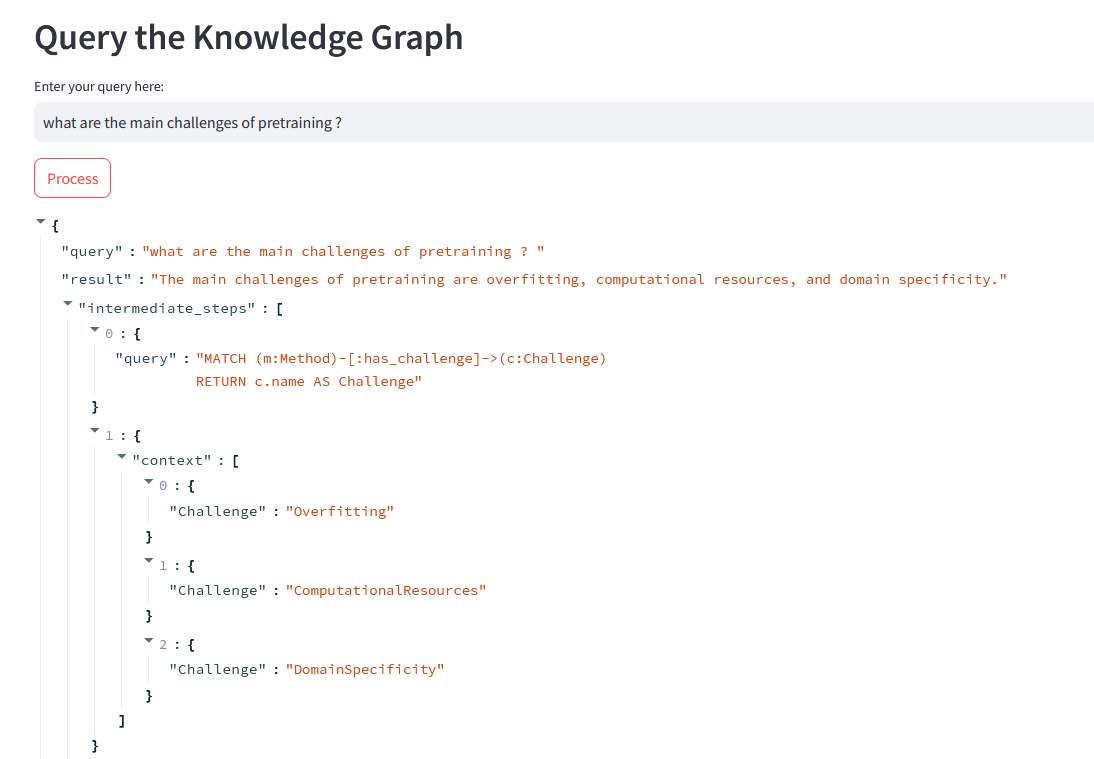
Finally, I tried a query in natural language, and the result is pretty satisfying !
Improving the draft
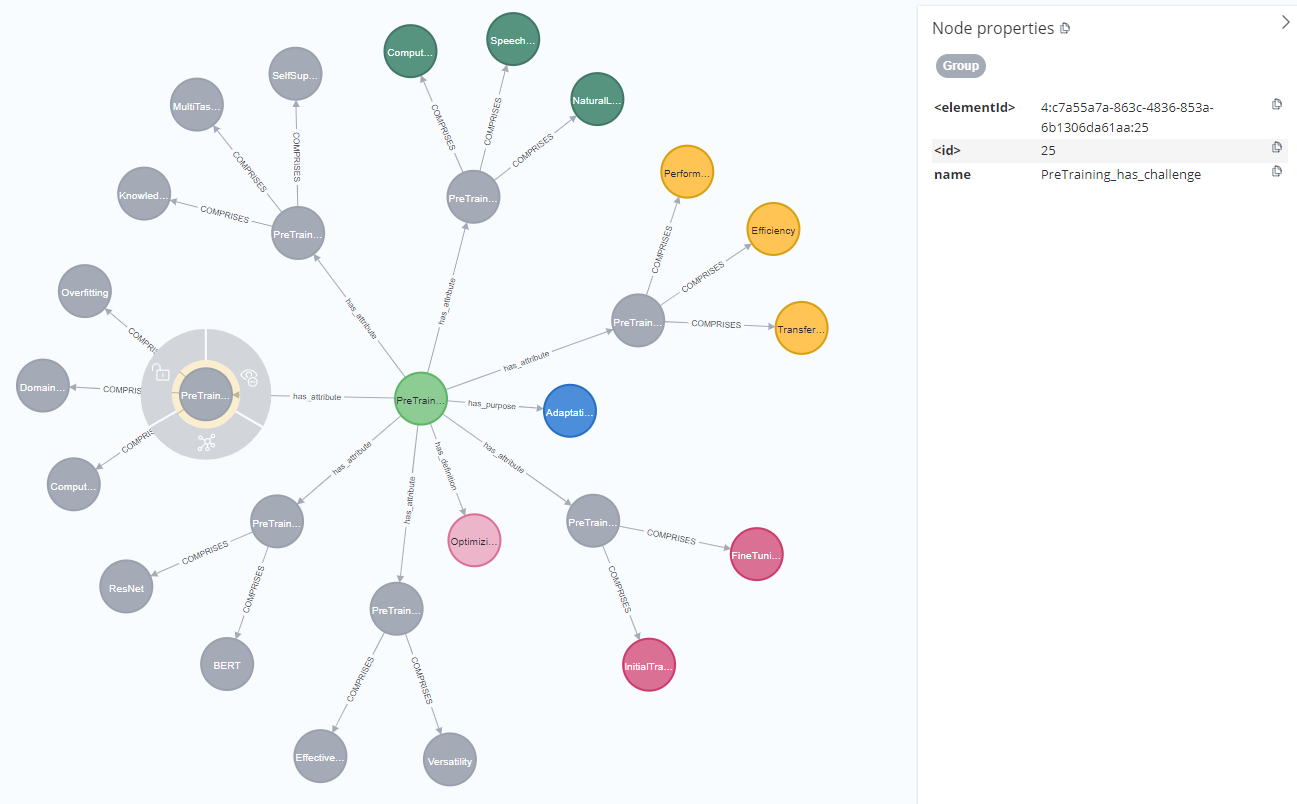
Grouping attribute nodes - false good idea
I tried grouping relationships under group nodes to improve visualization in neo4j browser but I did not think about the resulting increase of cmoplexity for the queries, so it was a bad idea. I think my main mistake was not thinking in terms of graph. Intuitively, it seems logical to group all examples under a same Examples node, retrieving attributes for a given node, seeing that it has an Examples node and then retrieving just this node, if I am looking for examples. Unfortunately in terms of graph traversal it means at least two hops for the query where by default it would only have been one hop.
Here is how it looked like:
Updating existing data
The next main challenge I face is how to add new data.
- how to prevent duplicate nodes and duplicate relationships? Not only perfect duplicates (which are the easiest to find) but also names that are almost the same or have the same meaning.
- how to fuse a new subgraph of knowledge into our current graph?
Exploring queries on graph
We now want to explore the different ways to make queries on graph.
- What queries work? What does not work? How can I fix it?
Some lessons learnt from this project
- As huggingface recommends, outputting code instead of JSON or formatted text like in neo4j tutorials proves to be more reliable.
- The main challenge is how to generate the graph objects from the input text.
- Instead of using a single prompt to extract data and do the conversion into Cypher I broke it down into several steps. Indeed, I remarked that generating Cypher is complicated for the LLM, so it struggles to do everything reliably at once. That is why I made the formatting into Cypher query an independent step.
- One must think about the application when building the graph. Depending on the application, nodes and relationships do not have the same meaning. I struggled a bit before understanding how I wanted to create my knowledge base; considering nodes as concepts and relationships as attributes.